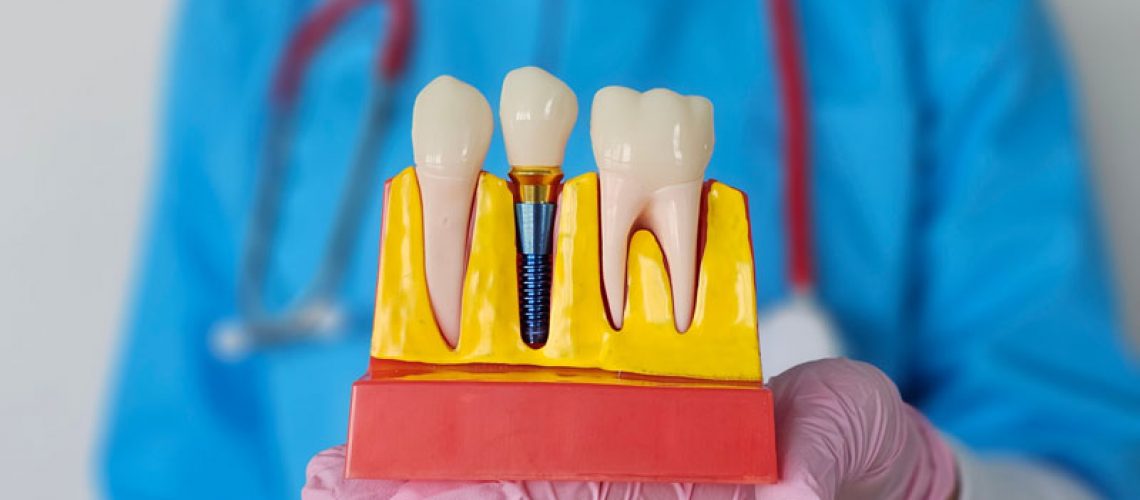
Dental implants have revolutionized the way individuals approach tooth restoration, offering a reliable and effective solution for missing teeth. These implants are small titanium posts surgically placed into the jawbone, acting as roots for artificial teeth. While the underlying concept of dental implants is consistent, the types available cater to different needs and circumstances. The diversity among these implant types arises from variations in their design, installation process, and the specific patient conditions they address. Delving into the different types of dental implants can help illuminate their benefits and how they contribute to a confident smile. Understanding these distinctions aids in making informed decisions regarding dental restoration needs.
Choosing the right dental implant involves careful consideration of the type that best suits the patient’s dental anatomy and lifestyle needs. Endosteal and subperiosteal implants represent two primary categories, each with unique characteristics. Endosteal implants are the most common, inserted directly into the jawbone and providing strong and stable support for prosthetic teeth. In contrast, subperiosteal implants rest on the jawbone and are suitable for patients who have insufficient bone height or cannot undergo bone augmentation. Recognizing the structural differences between these implant types paves the way for tailored dental solutions. Conversations with dental professionals are key in evaluating which option is optimal for achieving long-term oral health.